Occupational Asthma is the most common respiratory disease among workers in industrialized countries. In this article, we will identify the characteristics of this type of asthma, and discuss how it can be treated | Forest Medical Equipment Calibration
Asthma is an inflammatory disease which causes a narrowing of the airways. Asthma attacks can be severe and can put the life of the patient in danger. “In some cases, it is the occupational environment that causes asthma,” says Professor Walter Vincken, Head of Pneumology at Brussels University. Immunological reactions to allergenic substances such as persulfate, flour or latex, cause the symptoms of asthma to appear. After prolonged contact with these substances, ranging over several months or years… “Barbers with persulfates, bakers with flour, and nurses or doctors with latex, among others, are the most at risk.”
Another, rarer variant of occupational asthma may be caused by acute accidental exposure to substances such as chlorine vapours, combustion fumes, etc. The symptoms of this form of asthma, called “occupational asthma” (or ‘reactive airway dysfunction syndrome’ (RADS) occur immediately after exposure to such substances.
How to recognise occupational asthma
A series of questions can put the doctor on the trail of occupational asthma. “Has asthma appeared after the start of the offending professional activity? In previous work, did the patient also have complaints of asthma? Do symptoms appear on contact with certain substances? Do the symptoms improve when the patient is not at work? “
The doctor can then proceed to a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis.
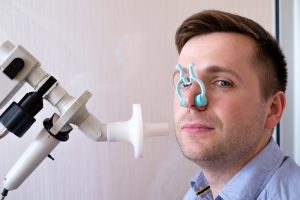
“One option is to equip the patient with a Spirometer. This device measures the maximum airflow a person can produce when exhaling. This measurement allows the patient to know the variations of his lung function during the day. The patient must measure his peak expiratory flow during and outside his work, several times a day. Significant variations can put you on the road to occupational asthma” explains Professor Vincken. “A diagnosis of occupational asthma can also be made by carrying out a provocation test during which the patient is exposed to the suspected substance (flour, latex …). The doctor then checks if it causes asthma in their patient.”
How do you treat occupational asthma?
“As with ordinary asthma, the main measure is to avoid exposure to the substance. The symptoms usually improve. It is most often recommended to the patient to change professional orientation,” explains Professor Vince. But in some cases, such as latex allergy, it is sufficient, for example, to use medical gloves made from another substance.
If this is not possible, or if symptoms persist, occupational asthma can be treated with medication. In recent years, new biological therapies have been used to improve the control of severe allergic asthma.
In severe asthma, inhaled corticosteroids (which decrease inflammation) are associated with the use of a long-acting bronchodilator (which relaxes bronchial muscle). However, the symptoms of severe asthma may remain abnormally frequent despite the treatments that have been initiated. This is called “severe, poorly controlled asthma”. In this case, the treatment must generally be re-evaluated.

The use of systemic corticosteroids (taken orally) may be considered in particular. These anti-inflammatory drugs act like inhaled corticosteroids on bronchial inflammation. They can pose another problem, however, long-term use of oral cortisone is accompanied by significant side effects: osteoporosis, diabetes, skin atrophy (thinning of the skin), weight gain, high blood pressure etc.
Severe allergic asthma: the emergence of biotherapies
For the last ten years, new drugs have been used in severe allergic asthma. These are “biological treatments”. Biological treatments are increasingly used to control the symptoms of severe allergic asthma. People with severe asthma have particularly pronounced and persistent symptoms that hinder their quality of life. Among these symptoms include: wheezing, coughing, feeling of shortness of breath which may be frequent during the day and at night; almost permanent bronchial obstruction; a rapid deterioration of the respiratory function as soon as the treatment is reduced or frequent exacerbations (sudden accentuation of symptoms), likely to cause a significant deterioration of the quality of life, repeated visits to emergencies or even hospitalisations.
Among these new generations of drugs are Omalizumab ( Anti – IgE) for cases of severe allergic asthma requiring regular use of systemic steroids. This additional treatment is administered as an injection subcutaneously, once or twice a month.
The mode of action of Anti-IgE?
Anti-IgE antibodies are monoclonal antibodies, that is, molecules that look like the antibodies our body naturally produces in case of infection, for example. These monoclonal antibodies are programmed to recognize and neutralize a specific target. Here, Anti-IgE is directed against another antibody, immunoglobulin E (IgE).
In people with asthma, IgE is produced by white blood cells in response to exposure to an allergen such as animal hair, pollen or mites. It plays a central role in triggering the cascade inflammatory reactions responsible for the symptoms of asthma. By blocking the action of these antibodies (IgE) by another antibody, Anti-IgE blocks the activation of this allergic cascade.
Anti-IgE: what side effects?
The side effects of Anti-IgE are low to moderate. Local skin reactions at the injection site are nevertheless possible.
Anaphylactic reactions (exacerbation of allergy) have also been observed in less than 1% of patients, which is why they should remain under observation after the first injections.
Anti-IgE: what results?
Anti-IgE reduces the frequency of exacerbations and hospitalizations, improving the quality of life of people with severe allergic asthma. They also make it possible to reduce the use of systemic steroids and, consequently, to limit the side effects that these drugs cause in the long term.

Forest Medical Equipment Calibration
Medical equipment calibration is incredibly important and should be done regularly. Sophisticated devices require more frequent checks because of their complexity and the number of different things that could become inaccurate. Once a test and calibration is complete devices should be certified to show that they meet all requirements and regulations.

